Gastric Bypass | Gastric Banding | Stomach Baloon | Weight Loss Treatment in Lahore | Pakistan
Gastric Bypass
The Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, also called gastric bypass, is considered the ‘GOLD STANDARD’ of weight loss surgery and is the most commonly performed bariatric procedure worldwide.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
RYGB restricts/limits food intake. RYGB also decreases how food absorption. Food intake is limited by a small pouch that is similar in size to the pouch created with AGB. Also, the food is directly sent from the pouch into the small intestine, that greatly affects the absorption of food. The food is absorbed differently because the stomach, duodenum, and upper intestine no longer come in contact with food.
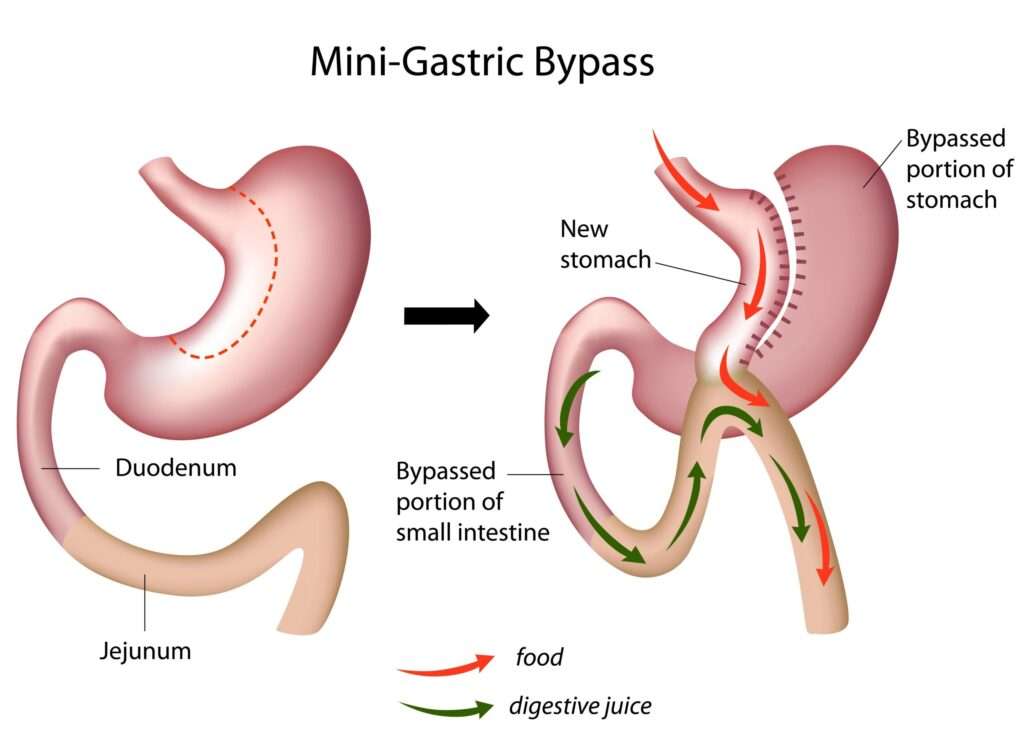
Fig: Gastric Bypass
The Procedure
This procedure comprises of two main steps.
1-First, a small stomach pouch, about one ounce or 30 milliliters in volume, is created by dividing the top of the stomach from the rest of the stomach.
2-Next, the first portion of the small intestine is divided, and the bottom end of the divided small intestine is brought up and connected to the newly created small stomach pouch. The procedure is completed by connecting the top portion of the divided small intestine to the small intestine further down so that the stomach acids and digestive enzymes from the bypassed stomach and first portion of small intestine will eventually mix with the food.
Mechanism of action
The gastric bypass works by following three mechanisms.
1-First, similar to most bariatric procedures, the newly created stomach pouch is considerably smaller and facilitates significantly smaller meals, which translates into fewer calories consumed.
2-Additionally, because there is less digestion of food by the smaller stomach pouch, there is alsoto some degree less absorption of calories and nutrients.
3-Most importantly, the rerouting of the food stream produces changes in gut hormones that promote satiety, suppress hunger, and reverse one of the primary mechanisms by which obesity induces type 2 diabetes. To Read More About Gastric Bypass Click Here.
Advantages
- Produce leads to significant long-term weight loss (60 to 80 percent excess weight loss)
- Restricts the amount of food that can be consumed
- May lead to conditions that increase energy expenditure
- Produces favorable changes in gut hormones that reduce appetite and enhance satiety
- On average typical maintenance of >50% excess weight loss
Disadvantages
- Is technically a more complex operation than the AGB or LSG and potentially could result in greater complication rates.
- Can lead to long-term vitamin/mineral deficiencies particularly deficits in vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate.
- Generally has a longer hospital stay than the AGB.
- Requires adherence to dietary recommendations, life-long vitamin/mineral supplementation, and follow-up compliance.